What Is The Normal Microbiota In Our Body?
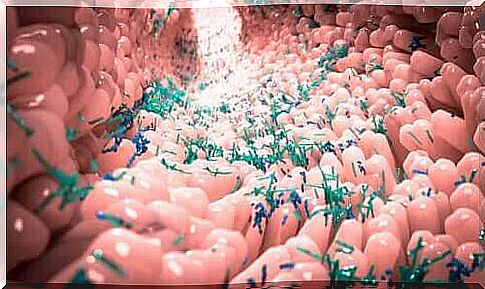
Bacteria are microorganisms that, despite their small size, play an important role in the functioning of the world. Scientists estimate that they represent 50% of the total biomass on the planet. Humans also show an indispensable relationship with them through normal microbiota.
In this article we will show you what a normal microbiota, also called a microbiome, in your body is and what it is made of.
What is normal microbiota?
Normal microbiota or microbiome is defined as the set of microorganisms that are often found in the body of healthy people, distributed in different parts of the body.
This interaction is a symbiotic relationship between the host and the bacteria since both parties benefit from the relationship. Some of the benefits are the following:
- Bacteria help with the digestion of food that humans cannot assimilate in other ways.
- They produce vitamins and compounds that you cannot get from other sources.
- They protect your body from colonization by other microorganisms that can be pathogenic, which is called microbial antagonism.
Normal microbiota is important for our physiological systems to work. Sources such as the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México estimate that humans have around 100 billion microorganisms in their bodies. This shows that we cannot think about our existence as it is today without the microbiome.
Human microbiota categories
The term flora is used incorrectly if we analyze the use of the word since it has been established that bacteria are not related to vegetables in any way. For this reason, it is better to refer to the different bacterial populations grouped according to their functions as microbial ecosystems.
The set with all these populations gives rise to normal microbiota, which we divide into two categories :
- Autochthonous microbiota: These are microorganisms that live in our body indefinitely or for a long time. They participate in quantifiable physiological processes and have evolved with our species by adapting to the environment we offer them.
- Allokton microbiota: These microorganisms appear in any habitat and can appear in our body accidentally or temporarily. They do not participate in physiological processes since the relationship with humans is based on random encounters.
This general designation can also be qualified according to the residence time of the organisms:
- Latent microbiota: This is the set of organisms that the host presents throughout the life cycle. In this case, the host is us. The population usually does not fluctuate significantly, and the symbiosis is complete.
- Volatile microbiota: This is the type that has continuous fluctuations in the population and is usually not important for the host’s survival. Factors such as season, age or medication can cause it to change.
Therefore , the bacteria in the intestinal tract will be an example of a natural and latent microbiota. They are necessary for the digestive system to function properly and remain with us throughout life.
What is normal microbiota made of?
In a healthy living being, internal tissues such as blood or the brain are free of bacteria. On the other hand, the external tissues and those surrounded by mucous membranes, such as the intestine, skin or throat, have plenty of symbiotic microorganisms.
Researchers estimate that the intestinal microbiota contains more than 400 species of bacteria. Furthermore: For every human cell, they estimate that there are 10 microbes in our body.
Covering all the significant species present in the normal microbiota is virtually impossible. For this reason, there are lists of the most common species by body region according to their usual, sporadic, rare or possible presence of pathogens. The microbiota has a very clear representation in certain regions such as:
- The skin, dominated by gram-positive bacteria.
- The intestine, where the intestinal flora can weigh around 1.5 kilos.
- The vagina, where the primary genus is Lactobacillus (96% of all microbes in the area).
- The mouth, which has one of the most complex and heterogeneous microbiota in the body.
An important microscopic world
As we have seen in a general way, the normal microbiota in the human body is infinitely complex. Certain ideas must be clear to us: some bacteria are essential and remain in the body forever, while others are only there temporarily.
These bacterial populations vary according to the region and the person, but the set of them all constitutes the normal human microbiota.