The Characteristics And Function Of Neurons

When you look at the function of neurons, and how they work, it is revealed that these cells are a sophisticated piece of natural “construction”. You may not be aware of it, but neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system, and they allow the body to control and coordinate all its activity.
The way neurons work makes it possible to transmit information to the body, both externally and internally, using a complex mechanism of chemical and electrical signals. The impulses can also be transmitted at a speed of 360 km per hour through certain nerve fibers.
Thanks to the way neurons work, we can withdraw our hands when we touch a burning hot surface, feel when something is soft, experience pain, know if something is cold and so on. These cells are like messengers in our nervous system.
The characteristics and function of neurons
Neurons are a cell type and are part of the nervous system. Their basic function is to receive and transmit information through electrical impulses. Neurons create extensive communication networks throughout the nervous system.
These cells have a star-like shape and a central body that contains the structure that keeps them alive. They also have several branches, within which there are many short and tuft-like dendrites. In addition, they have a fairly long branch, called the axon.
People previously believed that the organism was not able to produce new neurons in the brain throughout life. However, a team of researchers from the Karolinska Institute of Medicine in Sweden conducted an experiment and found that this is not the case. The brain can produce up to 1400 neurons per day, thanks to a process known as “neurogenesis”.
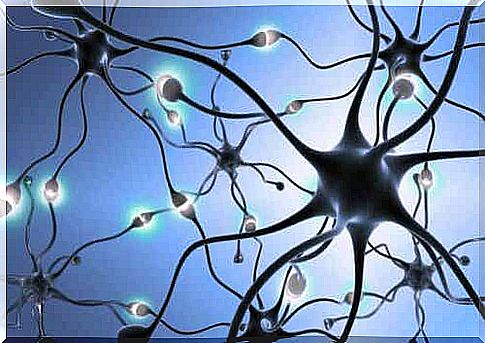
Neuronal structure
As mentioned above, neurons consist of three elements. Let’s look at each of them:
- The body, or soma, contains all the elements a neuron needs to be viable
- Dendrites are extensions that receive the nerve impulses sent by other neurons through the synaptic process.
- Finally, axon or neurite is a thin, long elongation, and its role is to transmit nerve impulses to other cells
All neurons basically have this structure, but are sometimes different from each other according to the functions they perform. Thus, there are three types of neurons:
- First, the unipolar neurons have a single branch that acts as a double pathway that acts as both a dendrite and an axon. They are characteristic of sensory neurons.
- Then there are the bipolar ones. These have two branches, one acts as a dendrite and the other as the axon. These are characteristic of the neurons in some parts of the eyes, ears and nose.
- Third, the multipolar is the most numerous type of neuron and has the classical structure of several dendrites in the form of a tuft, in the receiving zone and a long axon in the exit zone. They are usually in the spinal cord and brain.
How do neurons work?
The structure of these cells determines how neurons work. Simply put, the neuron receives an electrical impulse through the dendrites. It then passes through the body, or soma, and then goes to other cells via the axon.
The axon releases a chemical called a neurotransmitter. This in turn reaches the dendrites of the next neuron and triggers the electrical signal that starts a new cycle like the previous one. In fact, each neuron can make thousands of connections.
There are several types of neurotransmitters that facilitate the various neuronal functions:
- Serotonergic secretes serotonin (mood)
- Dopaminergic secretes dopamine (pleasure)
- GABAergic secretes GABA (inhibitory neurotransmitter)
- Glutamatergic secretes glutamate (memory and recall)
- Cholinergic excretion of acetylcholine (multifaceted)
- Noradrenergic secretes noradrenaline / noradrenaline (increased heart rate and blood pressure)
- Vasopressinergic secretion vasopressin (a homeostatic regulator)
- Oxytocinerg secretes oxytocin (affection)
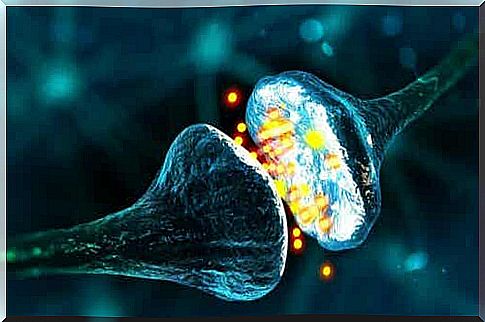
Other facts about the function of neurons
As you can see, neurons are small messengers in the organism, since their main function is to receive and transmit information. They receive and deliver it to other neurons as well as to muscles and glands.
So now you know that neurons have three main functions: sensory, integrative and motor. The sensory function allows us to perceive internal and external changes, such as heat, light and so on. Furthermore, the integrating function processes received information to provide an appropriate response. To cover ourselves when we are cold, for example.
Finally, motor function causes muscles and glands to act, or not, as needed. There are neurons in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), but these cells are also in the peripheral nervous system. The central nucleus is the ganglion located inside the digestive system.